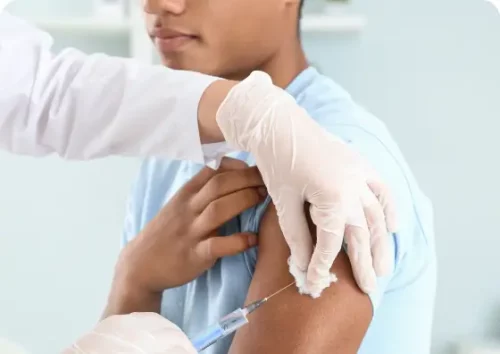
Allergy Shots
Allergy shots are administered on a regular basis exposing the body to a little amount of an allergen to establish immunity.
learn moreThe Allergy Center at Brookstone has Board-Certified Allergists closer than you think. Request an appointment today to get relief from allergies and asthma – and get back to living!
706-324-4012Schedule an appointment and get allergy and asthma relief.

Now Partnering with AllerVie Clinical Research
We are excited to partner with AllerVie Clinical Research and bring cutting-edge treatments and medical advancements to patients locally who need them most! The Allergy Center at Brookstone is proud to be part of the AllerVie Health network, which gives us the opportunity to leverage their national network and its resources to expand services, increase access to care, and bring you the latest advances in allergy, asthma, immunology, and clinical research.
Learn MoreLooking for a local asthma or allergy specialist near you? Our board-certified doctors understand unique allergy and asthma issues affecting those in and around Columbus, Georgia. Call us today to schedule an appointment and start feeling your best!
Hours of Operation: |
Shot Hours: |
| Monday: 8 am – 5 pm | 9 am – 5:30 pm |
| Tuesday: 8 am – 5 pm | 9 am – 5:30 pm |
| Wednesday: 7:30 am – 4:30 pm | 7:30 am – Noon |
| Thursday: 8 am – 5 pm | 9 am – 5 pm |
| Friday: 8 am – 5 pm | 9 am – 5 pm |
| Closed Saturday & Sunday | Closed Saturday & Sunday |
Shot room closes Noon-1:30 p.m. daily, except Wednesdays when the shot room does not reopen after lunch.

The Allergy Center at Brookstone in Columbus, Georgia provides individualized, state-of-the-art healthcare to patients and their families with asthma and allergic disease.
We care for patients with asthma, rhinitis (hay fever symptoms), allergic conjunctivitis (allergy eyes), chronic ear infections, sinus infections, eczema, hives, food allergies, and insect allergies.
We share a common vision of helping our patients of this community enjoy longer, healthier and more productive lives. To meet the needs of all our patients, we offer well visits, sick visits, allergy testing and much more!
Allergy/Immunology is the only medical specialty of our medical group and we are the only Board Certified Allergists within a 50-mile range. As a result, we are able to place the medical needs of our patients firsthand foremost by offering an uncompromising level of care to our patients.
Our office is a fragrance-free facility. The chemicals used in scented products can make some people sick, especially those with fragrance sensitivities, asthma, allergies and other medical conditions. We ask that all patients not wear perfume, cologne, aftershave or any other scented products when visiting our office.
AllerVie Health acquired the Allergy Center at Brookstone in September 2021, and is privileged to serve patients in the Columbus community. As part of the national AllerVie Health network, we are committed to providing high-quality allergy and asthma care and continuing to serve the Columbus and surrounding Georgia communities.

Allergy Shots
Allergy shots are administered on a regular basis exposing the body to a little amount of an allergen to establish immunity.
learn more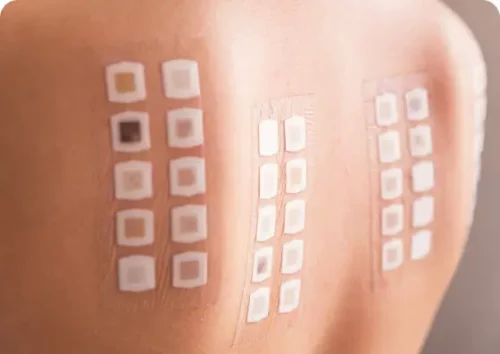
Allergy Patch Testing
Allergy patch testing is a common test used to confirm the cause of allergic contact dermatitis.
learn more
Skin Allergy Testing
This is less invasive than blood tests and is a good alternative for patients who don’t like needles.
learn more
Pulmonary Function Tests
These tests help your provider diagnose and monitor asthma symptoms by measuring your overall lung health.
learn more
In partnership with AllerVie Clinical Research our patients have the opportunity to participate in the future of medicine. We have opportunities for patients to participate in asthma research, eczema research, food allergy research, immunodeficiency research and other clinical studies. Visit our clinical research website for a list of ongoing active studies.
Learn More About Clinical ResearchWe are dedicated to improving quality of life, helping each patient that walks through their doors get back to enjoying the activities that make them happy — without worrying about allergies standing in their way.
Make an Appointment